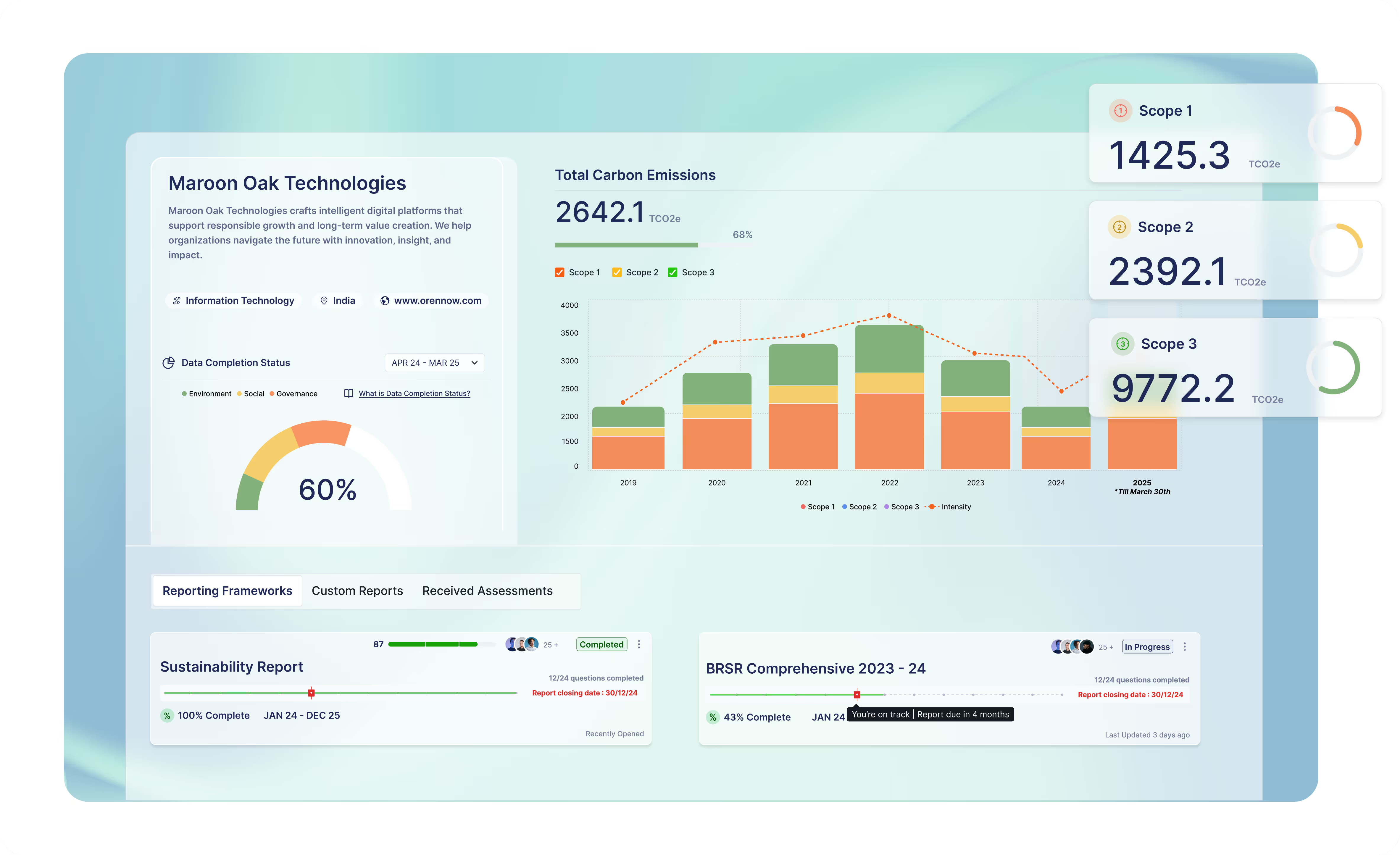
ESG Data Management Best Practices: Ensuring Integrity and Impact

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are increasingly important to investors, consumers, and regulators. Companies are under pressure to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and social responsibility, and this requires accurate and reliable ESG data. Effective ESG data management is essential for organisations to track their performance, meet reporting requirements, and make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals.
Accurate ESG data provides insights into an organisation's environmental impact (e.g., carbon emissions, energy usage, waste management), social responsibility (e.g., diversity, equity, and inclusion, labor practices, community engagement), and governance metrics (e.g., board composition, executive compensation, risk management). This article explores the best practices for ESG data management, emphasising the importance of data integrity and maximising impact.
Establishing a Clear ESG Data Framework
A robust ESG data framework is the foundation for effective data management. This framework should clearly define the organisation's ESG objectives, identify key performance indicators (KPIs), and establish processes for data collection, validation, and reporting. Choosing the right framework is essential, as it can influence a company's reputation, funding, and operational license.
1. Defining Objectives
Start by clearly articulating what you aim to achieve with your ESG data. Objectives may include:
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements and reporting standards.
- Performance Tracking: Monitoring progress towards ESG goals.
- Stakeholder Communication: Providing transparent and reliable information to investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
- Continuous Improvement: Identifying areas for improvement in ESG performance for improvement of ESG ratings or to drive cost reductions.
2. Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
It is crucial to connect your business model and ESG materiality to your sustainable business case. Prioritise the most important ESG topics and risks when considering data collection. For example, if climate change poses a significant risk to your business, track climate risk data and KPIs to monitor and communicate these risks to stakeholders. Select KPIs that are material to your business and stakeholders. These should align with industry standards and frameworks such as those shown in the table below:

3. Data Collection and Integration
Identify all potential data sources, both internal and external. Internal sources may include HR systems, procurement records, and energy consumption data. External sources may include supply chain partners, government databases, and ESG rating agencies. Implement automated data collection tools such as Oren Sustainability Hub where possible to reduce errors and save time.
Ensuring Data Quality and Integrity
High-quality data is essential for accurate ESG reporting and informed decision-making. Implement processes to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. High-quality data affects ethical reporting, increases investor trust, provides better visibility into ESG risks, enables effective planning for risk mitigation, optimises investments and asset management, and ensures continued regulatory compliance. Poor-quality ESG data can lead to operational inefficiency, reputational damage, and greenwashing accusations.
1. Accuracy
Establish data validation protocols to verify that data is correctly captured and reflects true performance. This may involve cross-checking data from different sources, using statistical validation techniques, and implementing data quality checks at each stage of the data management process.
2. Completeness
Ensure that all relevant data is captured and that there are no gaps that could lead to misinterpretation. This requires a thorough understanding of the organisation's ESG objectives and the KPIs used to measure performance.
3. Consistency
Maintain consistency in data definitions, units of measurement, and reporting periods. This is essential for comparing ESG performance over time and benchmarking against industry peers.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Use data analytics tools to identify trends, perform benchmarking, and generate insights from ESG data. Develop clear and concise reports for internal and external stakeholders that accurately reflect ESG performance. Transparent ESG reporting allows companies to openly communicate their impact on key areas such as climate change, human rights, and corporate governance. This transparency strengthens stakeholder trust, which is essential for maintaining a positive reputation in the market.
1. Analytical Tools
Utilise data visualisation and analytics tools such as Oren Sustainability Hub to turn complex ESG information into useful insights. These tools can help companies spot trends, compare performance, and share results clearly. With interactive dashboards and visual reports, these tools make it easier to engage stakeholders and make decisions based on data.
2. Reporting
Align ESG reporting with established sustainability reporting standards and frameworks to ensure consistency and comparability. Involve stakeholders in the reporting process to ensure that the reports meet their information needs and to enhance the credibility of the data.
Technology and Tools
Technology plays a pivotal role in streamlining ESG data management. ESG reporting software can lead to streamlined processes, cost savings, and enhanced stakeholder communication. Here are some key technologies organisations can adopt:
k.webp)
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples of successful ESG data management can provide valuable insights.
- Prologis: This leading logistics real estate company used ESG data to optimise energy performance across its properties, leading to significant energy cost reductions and a decreased carbon footprint. Prologis analysed consumption data to pinpoint areas for improvement and invested heavily in energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy installations.
- Unilever: This multinational consumer goods company committed to sourcing its raw materials sustainably. Through ESG data analysis, Unilever identified suppliers with strong social and environmental practices and collaborated with them to ensure responsible sourcing of ingredients like palm oil, cocoa, and tea.
- Corficolombiana: This Colombian financial services company implemented a system to systematically gather ESG data from each portfolio company using customised, industry-specific forms. This enabled continuous, accurate assessments of both individual investments and the overall portfolio of Corficolombiana, identifying opportunities for growth and potential risks.
Challenges and Risks
While ESG data management offers significant benefits, organisations may encounter challenges:
1. Data-related challenges:
- Diverse data sources and standardisation: Companies often deal with a mix of data from various vendors, each using its own unique identifiers. This lack of standardisation complicates ESG screening and analysis.
- Data fragmentation: Data may be scattered across different departments and systems, making it difficult to collect and consolidate.
- Data quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be challenging, especially when dealing with diverse data sources.
- Volume and velocity of data: Handling large volumes and rapid inflows of ESG data can be challenging due to limited capacity in resources and infrastructure.
2. Regulatory challenges:
- Evolving regulations: Keeping up with changing ESG reporting standards and regulations can be complex and time-consuming. The lack of unified standards and evolving regulations pose significant challenges to ESG reporting.
- Compliance and regulatory reporting: Compliance with standards such as SFDR presents challenges, particularly for firms with limited data capabilities.
3. Expertise challenges:
- Lack of expertise: Many organisations lack skilled professionals to manage and interpret ESG data effectively.
- Integration and accessibility issues: Data silos and accessibility issues are common problems. Seamless integration of ESG data into current systems is crucial to prevent operational disruptions.
- Operational efficiency and cost management: Efficient management of ESG data is crucial for cost reduction and enhanced productivity.
- Scalability and flexibility to adapt: The demand for ESG data is growing, and firms often struggle to respond to new demands quickly.
Measuring the Impact of ESG Data Management
Measuring the impact of ESG data management is crucial for demonstrating the value of these efforts and identifying areas for improvement. This can be done by tracking key metrics, such as:
- Improved ESG Scores: Monitor ESG ratings from agencies and investors to assess the impact of data management on the organisation's overall ESG performance.
- Reduced Costs: Track cost savings associated with improved resource efficiency, waste reduction, and reduced environmental impact.
- Increased Investor Confidence: Assess investor engagement and sentiment towards the organisation's ESG performance.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Monitor media coverage and stakeholder feedback related to the organisation's sustainability efforts.
- Improved Employee Engagement: Track employee satisfaction and engagement with the organisation's ESG initiatives.
Conclusion
Effective ESG data management is essential for organisations to navigate the complexities of ESG reporting, meet stakeholder expectations, and drive sustainable growth. By establishing a clear framework, ensuring data quality, implementing strong data governance, and leveraging technology, companies can unlock the full potential of their ESG data and create a positive impact on the environment and society. Accurate and reliable ESG data empowers organisations to make informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.