How to Accurately Calculate CO2 Emissions: A Comprehensive Guide

In today’s world, calculating CO2 emissions has become essential for companies striving for sustainability and carbon neutrality. With increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability, businesses must understand their carbon footprint to make informed decisions about reducing their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This article explores various methods to calculate CO2 emissions, offering insights into different strategies and tools to measure and manage carbon output effectively.
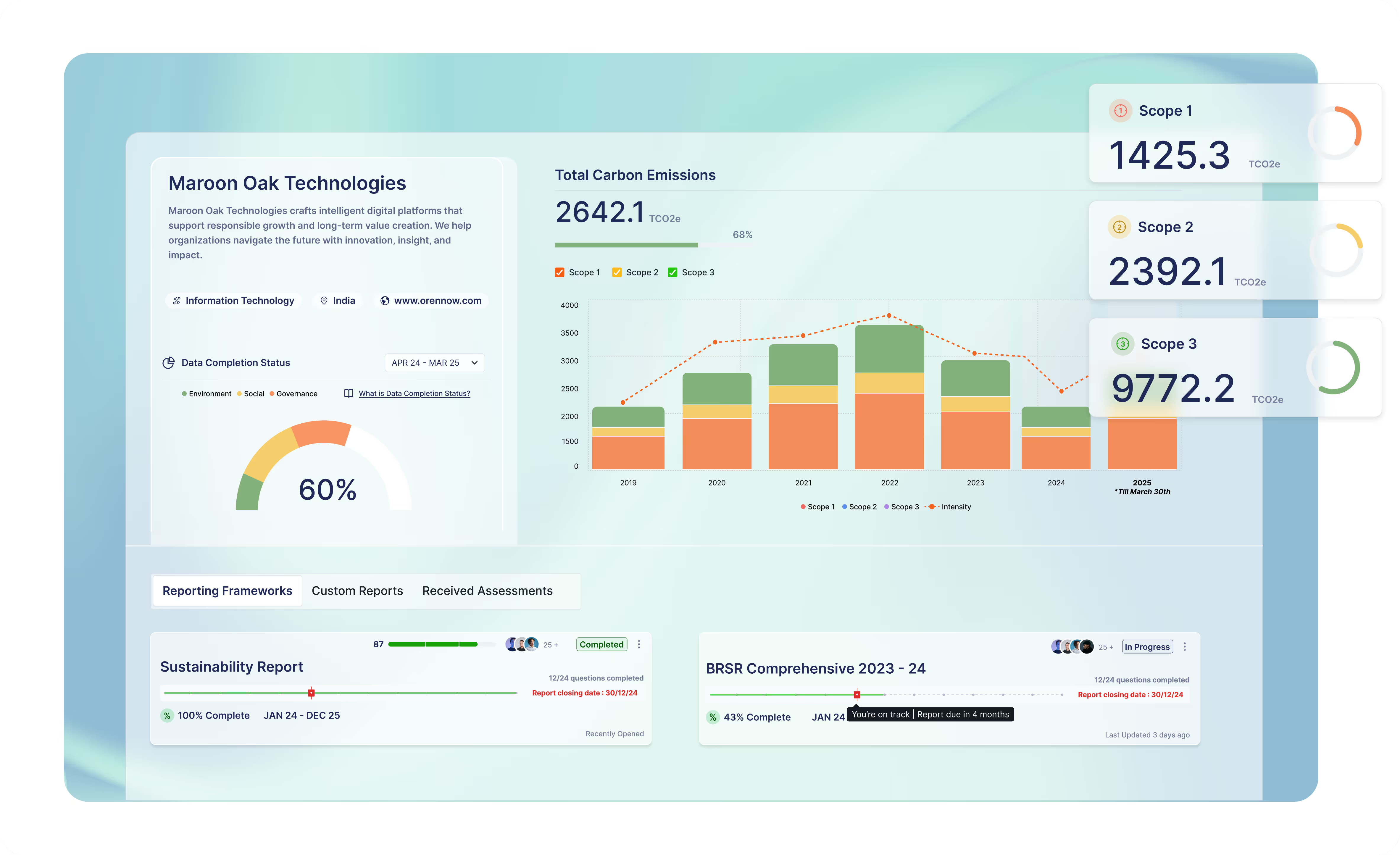
Understanding the Corporate Carbon Footprint
The Corporate Carbon Footprint (CCF) quantifies the total GHG emissions from a company's direct and indirect operations. Achieving carbon neutrality requires a thorough understanding of CCF, which encompasses all scopes of GHG emissions. To effectively measure your carbon footprint, consider the following steps:
- Identify Emission Sources: Classify activities related to emissions into Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 categories.
- Conduct a Materiality Assessment: Evaluate different emission sources to determine their impact.
- Compile Emission Data: Gather and analyse data from each emission source.
The GHG Protocol and ISO 14064 provide guidelines for calculating CCF, ensuring accuracy and consistency in measurement.

Fuel Consumption-Based Emission Calculations
Fuel consumption is a significant source of CO2 emissions for many businesses. Accurate measurement involves:
- Tracking Fleet Fuel Usage: Record gasoline or diesel consumption from company vehicles and apply emission factors to estimate CO2 output.
- Monitoring Facility Fuel Consumption: Measure natural gas or coal usage in industrial settings and calculate emissions based on fuel-specific factors.
Electricity Consumption-Based Emission Calculations
Electricity consumption also contributes to a company’s carbon footprint. Methods include:
- Regional Grid Emission Factors: Use local grid emission factors to estimate CO2 emissions from electricity used in office buildings or manufacturing facilities.
- Utility Bill Analysis: Review energy consumption data from utility bills and apply relevant emission factors to calculate CO2 emissions.
Activity-Based Measurements
Understanding emissions from specific activities helps target reduction efforts:
- Transportation Activities: Collect data on fuel use, vehicle mileage, and types to estimate transportation-related CO2 emissions.
- Energy Usage in Operations: Track energy consumption across various departments to determine emissions associated with specific processes.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) provides a comprehensive view of a product's or service’s carbon footprint by examining its entire life cycle:
- Product Life Cycle: Analyse emissions from raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, usage, and disposal.
- Service Life Cycle: Assess the carbon footprint of services, such as software platforms or consulting, through their lifecycle.

Utilising Supplier Data and Reporting
Supplier emissions play a crucial role in a company’s overall carbon footprint. Strategies include:
- Request Supplier Emission Data: Obtain emission data from suppliers who significantly impact your carbon footprint.
- Collaborate with Suppliers: Work with key suppliers to gather and integrate their emission data into your carbon accounting.
Leveraging Carbon Accounting Software
Carbon accounting software simplifies the emission measurement process by automating data collection, calculation, and reporting:
- Automated Data Management: Implement software that integrates with various data sources to streamline emissions tracking.
- Centralised Reporting: Use platforms that centralise emission data, making it easier to manage and report on carbon footprint.
Conclusion: The Path to Carbon Neutrality
Reducing CO2 emissions is crucial for achieving carbon neutrality and supporting environmental sustainability. By measuring CO2 emissions accurately and implementing effective reduction strategies, businesses can make significant strides toward their sustainability goals. Understanding the various methods of CO2 emission calculation—ranging from fuel and electricity consumption to life cycle assessments and supplier data integration—equips companies with the knowledge to make informed decisions and foster a sustainable future.



.webp)