The Evolving ESG Landscape in India: A Positive Shift Towards Sustainability

The landscape of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) in India is undergoing significant transformation. As investors and stakeholders increasingly prioritise not only financial returns but also positive social and environmental impacts, this shift marks a pivotal change in India's approach to sustainable development. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this transition, underscoring the need for more robust sustainability practices. Notably, the State Bank of India (SBI) has introduced a policy for ESG-compliant lending, signalling a broader movement towards integrating ESG criteria into financial decision-making.
The Rise of ESG Funds in India
The ESG investment space in India has gained considerable traction, with several key developments shaping its growth. As of now, only two asset management companies (AMCs) in India are signatories to the United Nations-supported Principles for Responsible Investment (UN PRI): SBI Mutual Fund and Kotak Mutual Fund.
1. Major ESG Funds and Their Impact
In recent years, the Indian market has witnessed the launch of significant ESG funds, each valued at $1 billion. Quantum Investors and Avendus are among the prominent players making substantial investments in ESG. Additionally, there are currently at least 17 mutual funds dedicated to ESG in the Indian market. Major AMCs such as Aditya Birla Sunlife, Axis Equity Fund, ICICI Prudential Fund, and SBI Magnum have introduced ESG-focused schemes.
AMCs are not only offering equity schemes under the ESG thematic category but are also launching exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and ETF funds of funds (FoFs). This expansion reflects a growing recognition of ESG investing's potential to deliver both financial returns and positive social impact.
2. Regulatory Changes and ESG Compliance
The regulatory landscape for ESG investing in India is also evolving. The market regulator has proposed that starting October 1, 2022, AMCs should invest only in securities with Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) disclosures. For international investments, AMCs can select global equivalents of BRSR as specified by the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI).

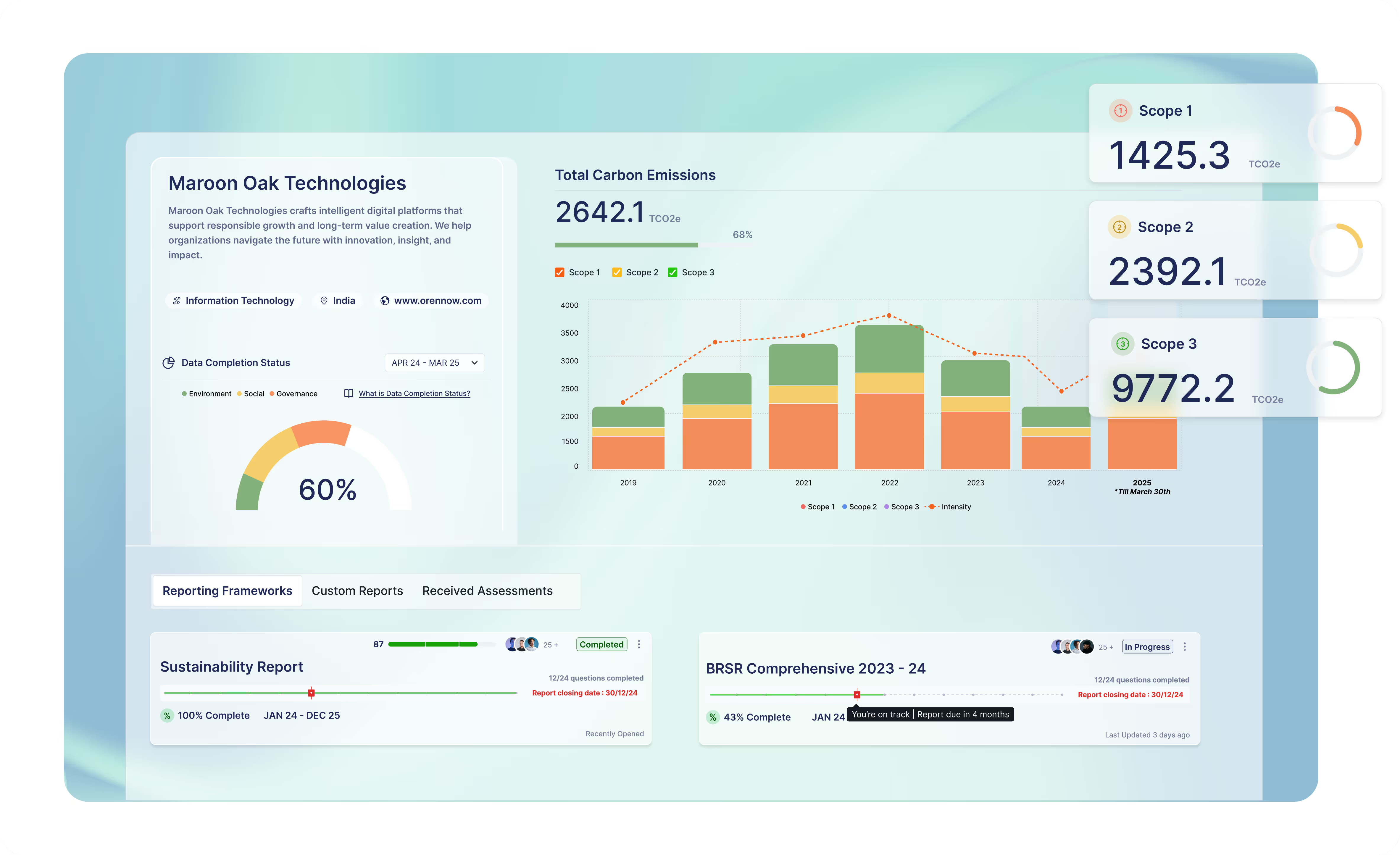
ESG Reporting: A Critical Component of Corporate Responsibility
Effective ESG reporting is crucial for companies aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Globally recognized frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and Integrated Reporting (IR) have been guiding companies in their sustainability reporting efforts.
Regulators are tightening the screws on ESG reporting, with certain companies now required to adhere to the BRSR (formerly Business Responsibility Reporting or BRR). The BRSR framework, which aligns with global standards, mandates comprehensive disclosure of ESG performance metrics.
For unlisted companies, there is an option to voluntarily adopt the BRSR-lite format for ESG reporting. This flexibility allows smaller or less complex entities to begin their ESG reporting journey without the extensive requirements of the full BRSR.
The Future of ESG in India: Trends and Expectations
The ESG landscape in India is set to evolve further, influenced by global sustainability trends and regulatory developments. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of ESG factors, not only for regulatory compliance but also for building long-term resilience and credibility.
Key Trends in ESG and Sustainability
- Carbon Neutrality and Net Zero Goals: Businesses are adopting carbon neutrality and net zero targets to mitigate their environmental impact. Understanding the difference between carbon neutral and net zero goals is crucial for effective climate action.
- Greenwashing Risks: As ESG reporting becomes more prevalent, the risk of greenwashing—where companies exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability efforts—has increased. Companies must ensure their ESG claims are backed by genuine practices and measurable outcomes.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations continue to guide global sustainability efforts. Companies in India are increasingly aligning their ESG strategies with these goals to contribute to global development and address pressing environmental and social issues.
Conclusion
India's ESG landscape is rapidly transforming, driven by evolving regulations, growing investor interest, and a heightened focus on sustainability. As the country navigates this shift, both companies and investors must stay informed and engaged with emerging ESG trends and reporting standards. Embracing comprehensive ESG strategies not only enhances corporate reputation but also contributes to a more sustainable and equitable future.