Creating an Effective SBTi Decarbonisation Roadmap

Introduction to SBTi Decarbonisation Roadmap
The Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) is a global-level organisation that validates and guides companies in setting the Science-Based Targets (SBTs) to ensure they support the 1.5°C climate goal. SBTs are measurable and climate-aligned goals. Companies set them to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions.
Decarbonisation: These targets (SBT) drive decarbonisation, which means the systematic reduction of carbon and other greenhouse gas emissions generated by the organisations. To help companies act, the SBTi provides a structured SBTi decarbonisation roadmap.
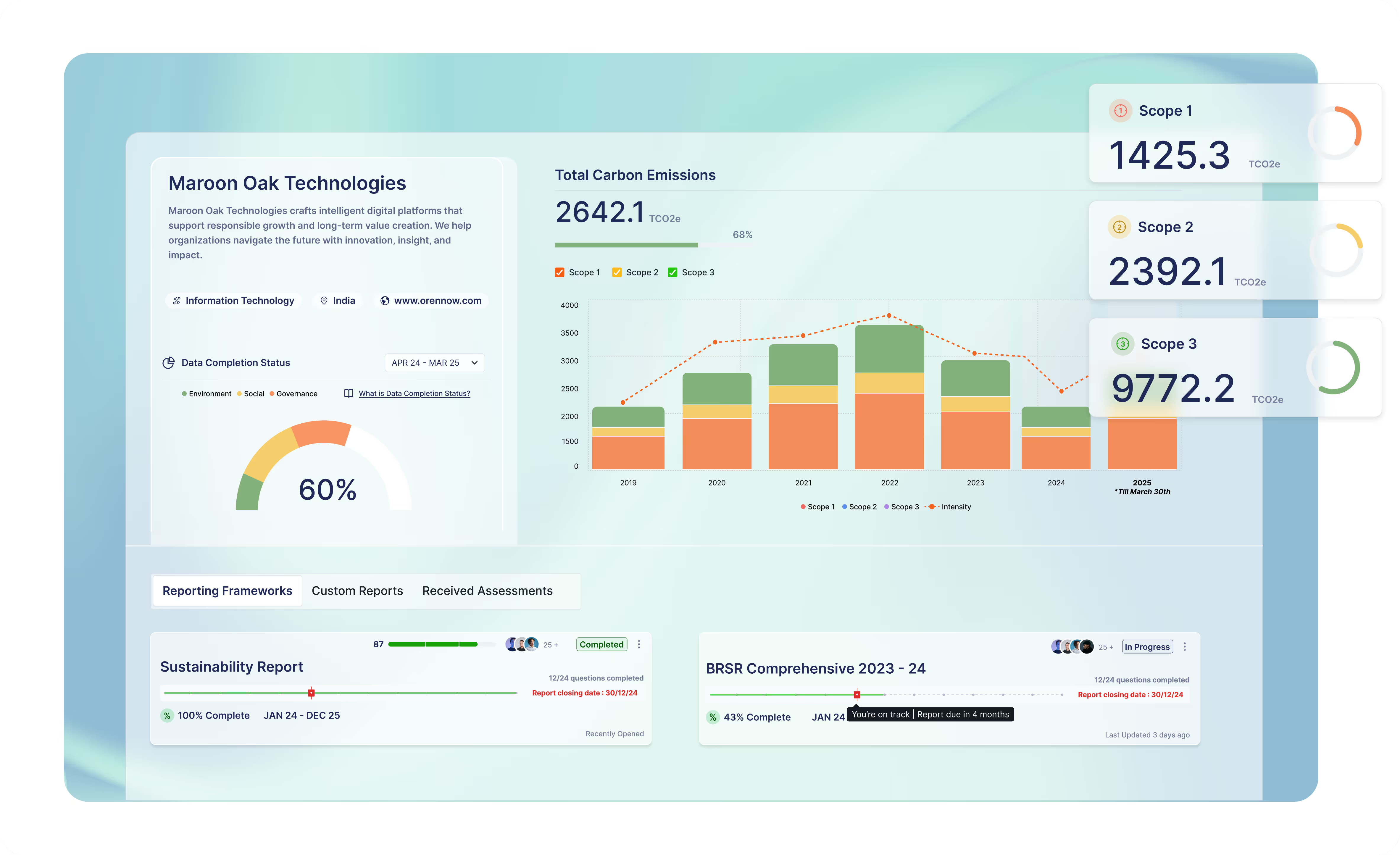
SBTi Decarbonisation Roadmap: The roadmap offers guidance for organisations to select a baseline year, to measure Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, to implement emission reduction strategies, and to track progress over time. It ensures that corporate climate action is aligned with global climate science. The SBTi roadmap supports companies in translating commitments into actionable plans.
Why an SBTi-Decarbonisation Roadmap Matters
An SBTi-aligned decarbonisation roadmap holds the following significance for the companies:
- Regulatory alignment and risk control: Keeps organisations ahead of evolving climate laws, carbon pricing, and compliance risks
- Enhanced investor confidence: Demonstrates long-term climate accountability and attracts sustainability-focused investors.
- Competitive advantage and innovation: Encourage low-carbon innovation in processes, products, and technologies.
- Cost-efficiency: Supports energy efficiency and renewable transitions that reduce long-term operating costs.
- Supply chain resilience: Extends decarbonisation across Scope 3 emissions and strengthens climate-aware partnerships.
Setting Science-Based Targets: The Foundation
Setting SBTs is feasible across industries. Here is what needs to be done:
Step 1: Commit
Submit the formal letter to register the organisation’s commitment to the SBTi. After registration, you will have 24 months to develop and submit your target.
Step 2: Select a Baseline Year
Gather the emissions data, categorise Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, and select the baseline year. The year should not be before 2015 and should be the same for both Scope 1 and 2 targets. Scope emissions must be measured according to the GHG Protocol using a common boundary approach across all company operations.
Step 3: Set the Target
Define the emission reduction goal using SBTi criteria and sector-specific guidance, if available.
Step 4: Submit for Validation
Send your defined targets to SBTi for technical review and approval.
Step 5: Communicate and Disclose
Share the targets publicly after validation and report progress annually through platforms such as CDP or sustainability reports.
Main Approaches Leading to Decarbonisation
Achieving decarbonisation is possible by choosing between the two freely available and open-source target-setting methods. Absolute Contraction Approach (ACA) and Sectoral Decarbonisation Approach (SDA): both these methods are used by SBTi to assess corporate emission reduction targets and both methods integrate seamlessly with the SBTi roadmap, ensuring sector-specific relevance. Here are some insights into both methods:
1. Absolute Contraction Approach (ACA)
It is a one-size-fits-all method that requires companies to achieve absolute reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. The method aligns with global decarbonisation pathways aimed at limiting warming. It is the preferred approach for most companies, with about two-thirds of SBTi-approved targets in 2020 using ACA.
2. Sectoral Decarbonisation Approach (SDA)
The Sectoral Decarbonisation Approach (SDA) is another way to set targets based on how much carbon different industries emit. It focuses on major polluting sectors such as road transport, aviation, basic materials manufacturing, and electricity production.
The method creates specific targets for each sector, recognising that some industries reduce emissions faster than others. Currently, SDA supports strict 1.5°C goals for the power sector while other industries follow slightly less strict pathways aimed at lowering emissions.
Building an Effective Decarbonisation Roadmap: Key Enablers
Effective implementation relies on several enablers, like:
- Leadership support: Strong commitment from top management and company-wide support helps achieve decarbonisation efforts.
- Digital tools: Accurate and real-time data collection and analysis are possible through digital platforms and AI. It enables decision-making and transparent progress tracking.
- Technology and innovation: Adoption of renewable energy, energy efficiency measures, and carbon capture technologies helps reduce emissions, especially in hard-to-abate sectors.
- Strategic financing: Access to green bonds, government incentives, and impact investments provides necessary funding to support decarbonisation initiatives.
- Collaboration and engagement: Involving employees, suppliers, customers, and investors fosters cooperation for managing complex supply chain emissions.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
The issues faced in the implementation of decarbonisation strategies, along with solutions, are as follows:
1. Internal Resistance
Resistance from teams worried about costs or disruptions can slow progress. Engaging leadership and promoting transparent communication helps. Sustainability teams should effectively exhibit the significance of working on climate goals for brand value improvement to address the issue.
2. Complex Scope 3 Emissions
Tracking emissions from suppliers and production use is difficult due to inconsistent data. Early collaboration with key suppliers and using standardised tools improves accuracy and avoids errors.
3. Data and Resource Constraints
High upfront costs and technical complexity require strong data systems and clear planning. Using trusted methods, setting short-term milestones, and adapting to regulatory changes help maintain momentum and build trust.
Conclusion
The SBTi decarbonisation roadmap provides a clear and science-based framework for organisations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions systematically. Following the SBTi roadmap can help companies align their climate actions with global goals. It also supports improving transparency and strengthening investor and stakeholder trust.
Strong leadership, data-driven strategies, and collaboration across the value chain are essential to overcome challenges. Thus, adopting the roadmap helps businesses drive innovation, manage risks, and build resilience for a sustainable future.
At Oren, we support companies in managing their decarbonisation journey from emissions quantification to decarbonisation targets and all the way to creating a long-term decarbonisation strategy.
FAQs
1. How frequently should science-based targets be reviewed and updated?
Science-based targets should be reviewed every five years. The five-year review cycle will start from the date of initial target validation or the most recent full update.
2. What are the most common barriers companies face in SBTi target implementation?
The common barriers faced by companies in SBTi target implementation is gathering data about Scope 3 emissions and financial and technological constraints. Internal problems like a lack of expertise and resistance to change are also among the considerable issues.
How can Boards effectively oversee the decarbonisation roadmap progress?
3. Boards can oversee decarbonisation by setting clear governance mechanisms, regularly reviewing emissions data, defining the company’s tolerance for climate-related risks, and ensuring alignment between actions and results. The boards should demand high-quality data and even obtain independent assurance.



-p-1080.avif)