Understanding GHG Emissions: From Accounting to Accountability

Introduction to GHG Emissions & Accounting
The heat-trapping gases released through human activities are termed Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions. The most common GHGs are:
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂), primarily from fossil fuel combustion
- Methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O), mainly from agriculture and waste decomposition
- HFCs, PFCs, SF₆, and NF₃, synthetic gases
GHG emissions undoubtedly have a significant impact! The planet is constantly warming up, and the global climate is changing. The United Nations reported 2015-2024 to have been the warmest decade on record. In 2022 alone, U.S. emissions reached 6,343 million metric tonnes of CO₂ equivalents. That is equivalent to cutting down almost 288 billion mature trees. Industrial processes went up 95%, and transport emissions rose 72% over the past 30 years.
Businesses must understand and take the right steps to manage these emissions. It should be a strategic action and considered an environmental responsibility. GHG accounting, or carbon accounting, can be the solution, as it shows a structured way to measure, report, and reduce emissions. It is crucial for credible ESG and effective decarbonisation strategies.
Strategic Importance of Carbon Accounting
Carbon accounting helps quantify GHG emissions across operations and supply chains. When emissions are measured accurately, and proper GHG accounting is in place, businesses can identify high-impact areas and optimise energy use to reduce costs.
GHG emissions accounting also helps with transparency. Companies can show verified environmental performance to stakeholders.
The major business advantages are:
- Operational Efficiency: Energy consumption is reduced, and resource usage is optimised.
- Cost savings: Utility bills and raw material requirements are lowered.
- ESG Credibility: Numerical proof for climate reporting becomes available, mitigating greenwashing risks.
- Investor and Customer Trust: Transparent emission data strengthens stakeholder confidence.
Important note: 100 energy companies are responsible for up to 71% of global industrial emissions. This makes accurate carbon accounting a strategic action for long-term financial and environmental resilience.
Key Standards, Scopes, and ESG Reporting Frameworks
A well-structured approach for measurement, management, and disclosure of GHG emissions is required to ensure accurate tracking, transparent reporting, regulatory compliance, and management of climate-related risks. Carbon accounting standards and ESG reporting frameworks provide that.
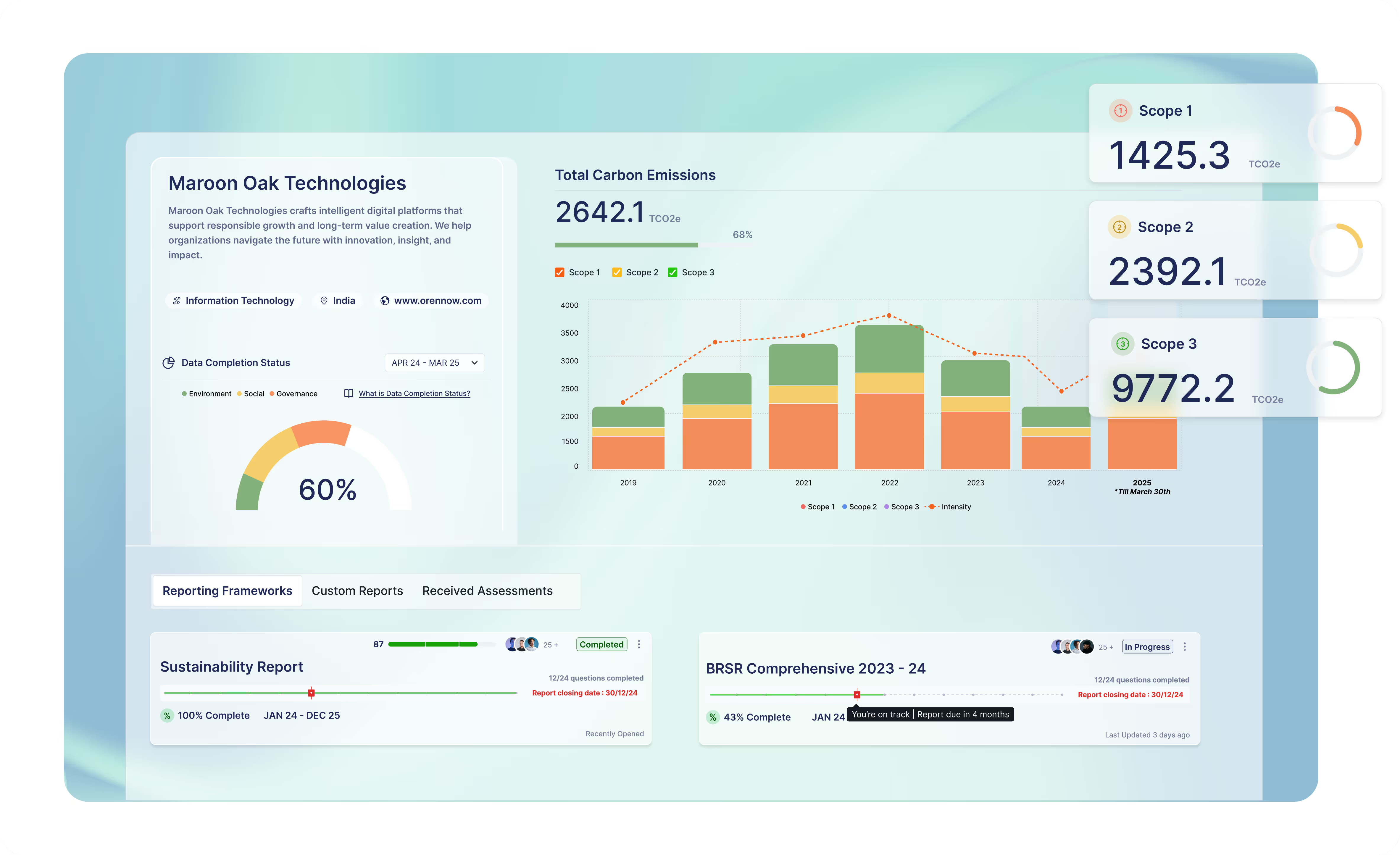
The GHG Protocol is considered the gold standard for carbon accounting. This protocol has classified emissions into three scopes:
| Scope 1 | Direct emissions from fuel consumed in owned or controlled sources, such as company vehicles or machinery. |
|---|---|
| Scope 2 | Indirect emissions generated from purchased energy, like electricity, heating, or cooling. |
| Scope 3 | Indirect emissions across the value chain, including purchased goods, transportation, waste, and employee commuting. |
Scope 3 represents the most complex area since this scope covers 15 categories, each with its own calculation approach, such as spend-based or activity-based, for calculation purposes. Initiatives, like the Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF), develop very detailed guidance, particularly for financial institutions.

ESG Reporting
In parallel, ESG reporting standards ensure transparency and accountability. Here are two popular guidelines:
- The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) provides comprehensive ESG disclosure frameworks.
- The Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) guidelines help companies in India to align reporting with sustainable practices.
Recent regulatory developments make reporting increasingly mandatory. For instance:
- The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) of the European Union and California’s Climate Disclosure Accountability Act require large companies to report scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
- IFRS S2 standards are being adopted globally, affecting over 100,000 companies.
Navigating Scope 3 Emissions: Challenges and Business Implications
Scope 3 emissions are by far the largest and most difficult part of a company’s carbon footprint because they involve activities upstream and downstream that are beyond the company’s direct control. These include purchased goods and services, transportation, waste management, employee commuting, and product use.
Challenges in Scope 3 of GHG accounting include:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Complexity | Multiple categories with varying data availability and quality. |
| Measurement Methodologies | Companies must choose between spend-based and activity-based methods. |
| Value Chain Engagement | Accurate reporting requires collaboration with suppliers and partners. |
The business implications are significant:
- Financial Risks: Scope 3 emissions often influence investor perception and regulatory compliance.
- Operational Opportunities: Identifying high-impact areas can inform efficiency improvements and supply chain optimisation.
- Reputation Management: Transparent disclosure strengthens ESG credibility and reduces greenwashing risk.
Scope 3 emissions can be more than 70% of a company’s total footprint, and for services and financial industry companies, it can be more than 90%. It becomes crucial for organisations to rely on structured methodologies, reliable data sources, and stakeholders’ participation to capture these indirect emissions and implement decarbonisation strategies accurately.
Innovations and Advancements in Carbon Accounting
In recent years, there have been significant innovations in carbon accounting, addressing both the methodological challenges and evolving regulatory expectations. Companies increasingly adopt hybrid approaches through the combination of spend-based and activity-based methods to attain increased levels of accuracy across scopes 1, 2, and 3.
| Spend-Based Method | Activity-Based Method |
|---|---|
| Uses financial data to estimate emissions | Uses actual usage and consumption data |
| Relies on average emission factors (a coefficient that indicates the rate at which an activity releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere) | Applies precise emission factors per activity |
| Quick to calculate, less data needed | Requires more data but gives detailed insights |
| Less precise due to general assumptions | More accurate and granular for key categories |
| Good for initial assessments or rough estimates | Ideal for high-quality reporting and decision-making |
These trends and developments indeed further empower organisations to move from simple measurement to actionable insight, integrating carbon accounting into strategic decision-making and supporting science-based targets.
The Role of Carbon Credits and Offsets in Emission Management
Carbon credits and offsets enable companies to mitigate residual emissions that cannot be eliminated through operational changes.
- Carbon credits refer to the reduction of one metric ton of CO₂ or the equivalent in other GHGs
- Carbon offsets are reductions achieved externally.
When an organisation invests in verified projects, like renewable energy, it can make up for unavoidable emissions. Carbon credits and offsets supplement net-zero goals and enhance corporate ESG credibility. Stakeholders receive assurance as the company actively addresses their climate impact.
Conclusion: From Accurate Accounting to Executive Accountability
There is a gap between data and actionable sustainability. One can bridge this gap with effective greenhouse gas accounting. With accurate emission measurements, following standards, and ESG reporting, organisations can:
- Identify high-impact interventions
- Optimise operations
- Communicate their climate commitment credibly.
With the increasing carbon footprint and the shift towards sustainability, GHG accounting can’t be treated as a mere compliance requirement. It is essential for executive accountability, informed decision-making, and long-term resilience in the race to net zero.
FAQs
1. What are the common obstacles in measuring Scope 3 emissions effectively?
Scope 3 involves complex value chain activities and data variability. Standardised reporting is often lacking here. To overcome these challenges, it is important to collaborate with suppliers, select the right methodologies, and rely on robust data collection.
2. What is the difference between carbon accounting and carbon management?
Carbon accounting quantifies GHG emissions. Carbon management, on the other hand, uses this data to come up with reduction strategies. Both play individual, important roles in lowering the carbon footprint of a company.
3. What are emerging best practices in leveraging carbon credits effectively?"
Some of the best practices include investing in verified, high-quality projects, combining offsets with internal reduction strategies, aligning credits with science-based targets, and maintaining transparent reporting for ESG credibility and net-zero objectives.



.webp)